US Dollar Exchange Rates of 30th September 2008
China Yuan 6.8451
Report from China
Emergence of China¡¯s forest plantations expands raw
material supply
Planting of China¡¯s fast growing and high yielding
plantations started in the early 1970s and developed
rapidly in the 1980s. The traditional wood industry, which
mainly depended on raw material from natural forests, was
heavily impacted by the implementation of China¡¯s natural
Forest Protection Programme in 1998 and in turn
cultivated and utilized fast growing and high yielding
plantations. In order to solve the shortage of domestic
wood resources, the State Council approved the
implementation of the Fast Growing and High Yielding
Plantation Programme, which is one of the six major
forestry programmes. The programme is mainly
distributed in 18 provinces and regions in the east of the
country. Over 13.33 million hectares of fast growth and
high yielding plantation bases will be established by 2015.
After the programme¡¯s completion, 140 million m3 will be
used to support the production of 13.86 million tons of
wood pulp, 21.5 million m3 of wood-based panels, 15.79
million m3 of large diameter timber, all consisting of 40%
of domestic timber demand. China¡¯s timber supply and
demand is expected to be balanced once these new
plantations are utilized.
The fast growing and high yielding plantation programme
has been proceeding well in recent years. According to
preliminary statistics for 18 provinces and regions, 52.22
million units of high yielding plantations have been
established and 3.3 million units of low quality production
forest has been planted, totaling 55.52 million units. Of the
total, 35% are for paper pulp plantation, 43% are for
wood-based panel plantation, 9% for large diameter timber
plantation, 4% for bamboo plantation, 2% for ¡®precious¡¯
species plantation. Of the total plantation area, 17.8£¥ were
planted by state-owned and collective forest farms, 10.3%
by foreign owned enterprises, 39.7% by farm households
and 9.5% by other entities. After completion, more than 15
billion yuan will have been invested. Of this total, 11% of
funds are from national investments and the others are
from self-financing entities, domestic loans and foreign
capitals.
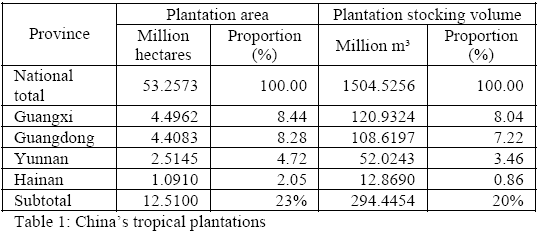
According to China¡¯s sixth forest resource inventory
report, the area of China¡¯s tropical fast growth and high
yielding plantation is 12.51 million hectares with 294.44
million m3 of stocking volume, which is distributed in
Guangdong, Guangxi, Yunnan and Hainan provinces (see
table 1). China¡¯s tropical fast growing and high yielding
plantation features Eucalyptus spp.
Currently there are 1.5 million hectares of eucalypt
plantations amounting to 30 million m³ by volume, with
investments mainly from private enterprises and foreign
owned enterprises. Experts predict that the area consisting
of eucalypt plantations will be 2.5 million hectares by
2010. Fifty percent of the raw material for making China¡¯s
pulp and paper feedstock is expected to be from eucalypt
plantations. The development of China¡¯s tropical eucalypt
plantations has not only increased farmers¡¯ incomes but
also has mitigated the pressure from demand for timber
and paper pulp.
China¡¯s tropical plantation eucalypts are mainly used to
produce paper pulp, wood-based panel and wood chips.
Using these products, wood chips, medium density
fiberboard (MDF) and plywood are exported. However,
official statistics on exports of these products are not
available. It has been reported that wood chips are
exported to Japan and South Korea.
China establishes quality control areas for exports
A number of supervision areas have recently been
established in China. Flooring export supervision areas in
Chanzhou City of Jiangsu Province, plywood export
supervision areas in Pizhou City of Jiangsu Province,
wooden products export supervision areas in Linyi City
of Shandong Province, and wooden products and
furniture export supervision areas in Dezhou City of
Shandong Province have been set up as a way to improve
the quality of China¡¯s exports. In addition, a wood, grass
and willow products export supervision zone is being
built in Heze City of Shandong Province.
The supervision zones are designed to align the quality of
China¡¯s wood products with international standards and
reduce trade frictions. This will be done by setting up
sound supervision mechanisms for wood products,
coordination mechanisms among wood products industry,
and quality, safety and standard tracking mechanisms for
wood products of export destination countries. Within
each supervision area, entry-exit inspection and quarantine
workers will help enterprises develop international quality
standard management systems, provide enquiry services
for the latest international standard and laboratory testing
services, help enterprises products meet international
standards of export destination countries and avoid trade
disputes effectively.
China turns attention to formaldehyde emissions in
California
It has been reported that California (US) has set new limits
on formaldehyde emissions. The state¡¯s Air Resources
Board approved an air toxics control measure for
formaldehyde emissions limits from composite wood
products in April 2008. The measure requires that
formaldehyde emissions from hardwood plywood,
particleboard, and medium density fiberboard be gradually
reduced by category. The new emissions limits are
scheduled to be phased in starting 2009 and fully
implemented in 2012. According to the standard in phase
one, formaldehyde emissions limits from plywood,
particleboard and fiberboard are 0.08ppm, 0.18 ppm and
0.21 ppm respectively and will be further reduced to 0.05
ppm-0.13 ppm.
China¡¯s companies exporting wood products mainly to the
US are paying more attention to the new regulation
enacted by California. The US is the largest market for
China¡¯s furniture exports. Therefore, China¡¯s enterprises
exporting furniture to the US are facing a new challenge
from California¡¯s new limits on formaldehyde emissions.
¡¡
|