|
Chevron and Weyerhaeuser to explore production of bio-fuels
In an effort to utilize wood-based by-products for biofuel, Weyerhaeuser and Chevron are
teaming up to further research this issue. According to Wood Based Panels International,
Weyerhaeuser will be contributing its knowledge and supply of cellulose and Chevron its fuel
technology expertise.
North America sees little growth for particleboard
In contrast to strong Eastern European trends where the capacity growth of particleboard is rapidly expanding, the
situation is less strong in North America. Starting in 2000, the North American particleboard industry on this
continent entered a transitional phase. Almost all the
major North American forestry companies ¨C including Weyerhaeuser, Georgia Pacific,
International Paper and Louisiana Pacific ¨C recently sold or shut down their
particleboard and MDF businesses.
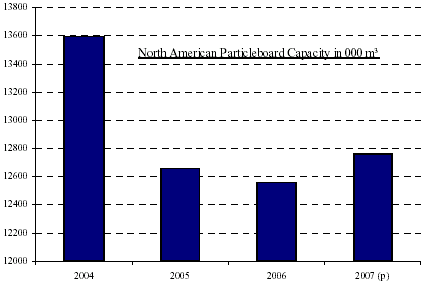
In the United States, the ongoing mill closures and
restructurings have not yet run its full course. On the other hand, the shrinkage of the production capacity and mill
closures in Canada came to an end in 2005 and last year witnessed a reversal of the downward trend. Similarly, in
Mexico, there has been a small upward movement in capacity during the past two years.
Despite this trend, the improvements in Canada and Mexico were not enough to
counterbalance the decline in the USA in 2006.
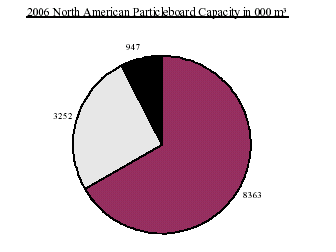
As a result of the lackluster investment activity in particleboard, the production capacity of wooden panels
was very limited in North America. Generally, producers are more inclined to achieve growth and boost their market
share through acquisitions rather than new capital projects in new particleboard mills. The largest particleboard
operator in North America is Flakeboard, with over 1.5 million m3 of capacity.
The North American industry is very cautious about the future demand and production costs for particleboard. The
usage for particleboard by the furniture industry ¨C suffering under a flood of imports from China and other
countries where operational costs are low ¨C is uncertain. Furthermore, some particleboard applications have been
negatively affected by the growing popularity of OSB. There are also signs that the slump in residential house
building will be longer than anticipated. Unlike MDF, particleboard has no laminate flooring market to stimulate the demand. In addition, costs are rising, particularly for
wood and resin.
North American offshore imports of overall engineered wooden panels rose by 47% in 2005 but particleboard is
only a minor portion of the total. This product is not economical to ship over long distances. Therefore, some
large European corporations may undertake some capital investments in North America, in particular if local
supplies should remain limited.
Mixed results for plywood and OSB in 2006
North American structural panel production reached a peak in 2006. Strong repair/remodelling as well as nonresidential
construction helped to offset the impact of declining US housing starts. Production in 2006 was up by
more than 2% on the previous year.
Production of OSB was up by more than 5% compared with last year. About 57% of the
production was located in the United States, and 43% in Canada. The growth of
production in the USA was particularly strong, at about 5.5%, while production of Canadian mills advanced by
slightly less than 5%.
In contrast to OSB production, North American plywood production in 2006 was almost 3% less than in 2005. The
production decline affected mainly ¡°sanded plywood¡±.
Overall, imports of offshore structural panels declined by
almost 5% last year, with plywood imports falling the most, well in excess of 10%.
¡¡
|