US
Dollar Exchange Rates of 31th May
2007
China Yuan
7.646
Report from China
¡¡
Forest industry chalked impressive performance in 2006
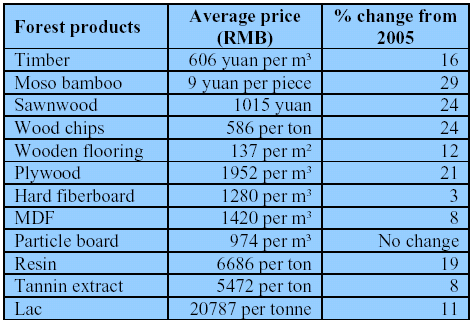
The total output value of China¡¯s forestry industry was RMB1.065 trillion in 2006, up by RMB219 billion or 26%
from 2005. Of the total, the output value of the primary forestry industry came to RMB471 billion, making up
44% of the national total, up 8% from 2005. The output value of the secondary forestry industry amounted to
RMB520 billion, exceeding the primary forestry industry for the first time, up by 49% from 2005. The output value
of the tertiary forestry industry reached RMB74.5 billion, a year on year increase of 21%.
The leading primary forestry industries¡¯ output value was RMB255 billion. Timber processing, wood and bamboo
products industry were the leading second forestry industries, with an output value of RMB272 billion. The
forest tourism industry was the leading tertiary forestry industry, with its outputs totalling RMB255 billion.
Due to the boost in the annual forest logging quota approved by the State Council, timber output in 2006 rose
by 19% to 66 million m3. Of the total, log yield grew by 22% or 11 million m3 from 2005 to 61 million m3 in 2006,
while fuelwood yield fell by 7% to 5 million m3. Sawnwood yield was 30 million m3, up by 67% from
2005. Of the total, tropical sawnwood yield made up 21.88%.
The output of wood-based panels in 2006 reached 74 million m3, an increase of 16%. Of the total, the output of
wood-based panels from tropical timber accounted for 2.46%. Plywood output was 27 million m3, up 8.5%;
fiberboard output 24.7 million m3, up 19.7%; and particle board output rose to 8 million m3, up 46%. MDF output
was 22 million m3; veneer output was 94 million m2, and other wood-based panel output amounted to 13.9 million
m3 .
The production of wood-based panels in China was still focused on six provinces, namely
Jiangsu, Shandong, Hebei, Zhejiang, Fujian and Guangxi. The wood-based panel output of the six provinces totalled about 50 million
m3, making up 68% of the national total. The wood-based
panel outputs in Jiangsu and Shandong Provinces ranked first and second, respectively, and
both provinces¡¯ output exceeded 10 million m3.
Bamboo output in 2006 was 1.312 billion pieces, up 14% from 2005. The output of China¡¯s resin was 915,400 tones,
up 36% from 2005.
The selling prices for China¡¯s major forestry industrial products in 2006 rose generally (see the following table).
In addition, there are 646 forestry projects using foreign capital in 2006, up by 157 from 2005. The actual utilized
foreign capital was US$781 million, a year on year decline of 32%, just 1% of the national total.
Greenpeace assails China for illegal timber imports
A recent report by Greenpeace International accused China of importing illegal tropical timber from Papua New
Guinea and Indonesia, making furniture from the timber, and then exporting the finished product. Cao Qingyao, a
spokesman for the State Forestry Administration (SFA) said at a press conference on 5 June 2007 that Greenpeace¡¯s claims were unrealistic. Cao noted that
China had been actively protecting global forest resources, promoting the improvement of the global environment,
and cracking down on timber illegal logging and related trade.
Cao explained that the development of China¡¯s forestry industry gradually moved from utilization of the domestic
market and resources to the utilization of international market and optimized allocation of global resources.
Timber and wood product imports were jointly supervised and managed by The State Forestry Administration,
Ministry of Commerce, and General Administration of China Customs, which guaranteed normal operation of wood products trade. China has also signed the International Tropical Timber Agreement, 1994, United
Nations Convention to Combat Desertification (UNCCD), the Convention on International Trade in
Endangered Species of Wild Fauna and Flora (CITES), the Ramsar Convention on Wetlands and Convention on Biological Diversity (CBD) and actively takes part in other
international processes that help combat illegal trade of timber.
Cao said that Chinese government encourages international community to insist on seven major
principles: state sovereignty; a dominant role for government action; sustainable forest
management; protection of international trade; global cooperation; realistic definitions,
assessment and reporting; and community involvement and gain benefits.
B&Q China stops selling merbau flooring
At the beginning of June, B&Q in China pledged to stop selling flooring made from merbau, in response to pressure
from Greenpeace International. It had been reported that B&Q headquarters in the UK made an announcement to its
global sub-stores to stop selling flooring made from merbau, primarily because merbau used in the store had
not been certified by an authoritative certification organization.
|