|
1.
CENTRAL/ WEST AFRICA
Prices for West African timber products largely stable
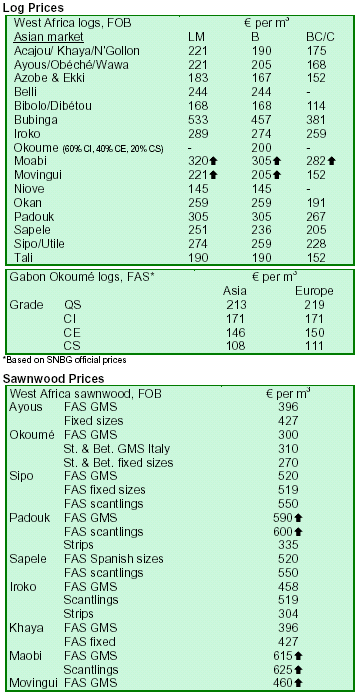
Prices for West African timber products remained unchanged in early April. Trade of both logs and lumber
continued steady. Cameroon mills reported firm log prices as the major concession areas are operated by the larger
operators. Medium and small sized mills fiercely compete for whatever limited supplies become available from the
informal logging sector. However, azobe and moabi
lumber were in short supply because of tight log supplies. Sipo and sapelli lumber were also
reported as rather scarce due to the same reason. Overall, market activity is steady
and likely to remain stable.
DR Congo cancels illegal logging contracts
The government of the Democratic Republic of Congo has recently cancelled 21 illegal logging
rights, covering nearly 3 million ha of forest, according to the Environment
Minister, Didace Pembe. He said that the forest concerned, which had been divided up between 16 companies, would
revert to public ownership by the end of April. The 21 cases concern forestry rights either obtained in violation of
the law or that had not been the subject of a request for conversion into a license
agreement. Holders of the cancelled rights, mostly small companies, have two weeks
to contest. Large logging firms which account for 70% of the country¡¯s production capacity, such as Safbois,
Sodefor, Siforco or Soforma, were not affected by the cancellations.
Korean group to build Congo railway in timber deal
A South Korean consortium has agreed to build a new 800-km railway in the Republic of Congo in return for
timber concessions, Gabriel Valere Aime Eteka, Cabinet Director at the Forestry Ministry, said. Timber is Congo¡¯s
second biggest export after oil, accounting for 7% of the GDP. A number of European and Asian companies hold
concessions to cut valuable hardwoods from large tracts of
tropical forest.
However, the densely forested north of the country is largely inaccessible, forcing its timber to be transported by
road for export from neighbouring Cameroon rather than from Congo¡¯s own port of Pointe-Noire, costing the
Congolese treasury an estimated 25 billion CFA francs (.38 million) a year in lost earnings. The Korean Resource
Consortium has agreed to build a railway from Brazzaville
to Ouesso in the Sangha region in the northwest of the country, and, in return, the government will grant it
forestry concessions, according to Mr. Eteka. The company would conduct a two-year feasibility study
before signing a final agreement with the Congolese government and starting construction work on the railway,
which would be used to transport timber from the new concessions, Mr. Eteka said. He added that the forestry
concessions granted to the consortium were valid for 15-30 years.
2. GHANA

3.
MALAYSIA
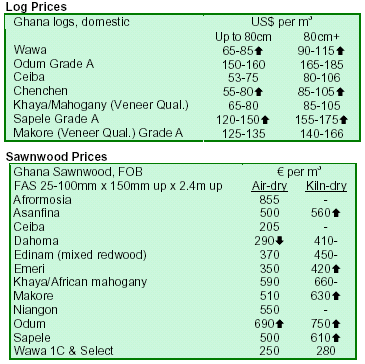
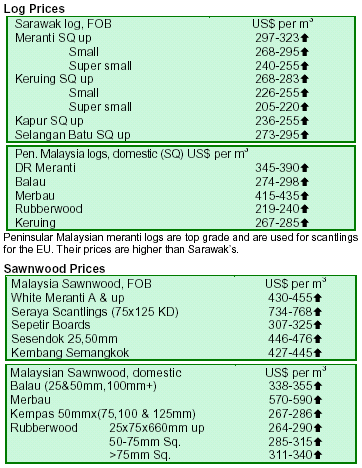
Prices edge up partly due to sliding US dollar
Prices of Malaysian timber products continued to rise in early April, partly due to the steady weakening of the US
dollar against the Malaysian ringgit. The Malaysian timber industry is optimistic of riding out the current softening
global economy. Optimism has been boosted largely by
continued buoyant demand for Malaysian timber products in the EU, China, Japan and the Middle East, particularly
in the UAE. This optimism is shared by the IMF latest assessment. According to the IMF, risks to the world
economy today are less than they were six months ago.
Gangsters damage the image of the forestry industry
The Malaysian Plantation Industries and Commodities Minister, Datuk Peter Chin Fah Kui, claimed that
gangsters were involved in running illegal logging operations due to the lucrative returns from trading in
unlicensed logs in the black market. According to him, the high demand for cheap logs had fuelled the entry of these people into the timber industry. He added that the problem
was getting more pronounced in Sarawak and several other states.
Mr. Chin informed that he would bring up the issue at the coming National Forestry Council meeting for
deliberation. He reckoned the need for tough actions to stop the illegal activity that was
damaging the image of the national forestry industry. Mr. Chin said that Sarawak was
facing problems in containing the involvement of gangsters in the timber trade because of the massive size
of the forests in the state.
EU suspends imports of ramin from Malaysia
The EU has suspended imports of ramin wood from Malaysia. The suspension was related to the listing of
ramin in Appendix II of CITES. The inclusion of ramin in the Appendix took effect in
January 2005, regulating its trade. A Sarawak Forestry Corporation senior official said
the suspension came as a surprise to both the federal and state authorities as the country had done what was required
under CITES. He added that the Sarawak Forestry was looking into the matter and discussing it with federal
authorities. He said the Natural Resources and Environment Ministry had called for an emergency
meeting to discuss the suspension in the federal capital.
Malaysia exports ramin wood mainly to the EU, USA and Japan. Exports are subject to a quota per state. Ramin is
one of the most valuable timber species and it is in good demand in the international market.
4.
INDONESIA
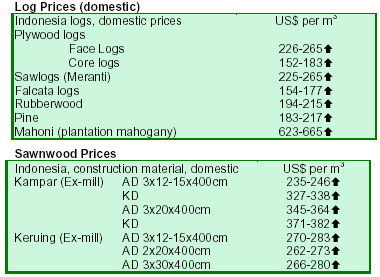
Indonesia urges not to buy products illegally produced
The Indonesian Environment Minister, Rachmat Witoelar, urged world consumers to stop buying products made
from illegally logged wood and said rich countries should pay the poor to preserve forests in the battle against global
warming. He said there were systems in place to distinguish stolen wood from legitimate products. Mr.
Witoelar, who said that furniture using illegally cut timber
from the Indonesian region of Papua was being sold in shopping malls as far away as the UK, urged other
countries to help oversee whether wood may have been logged illegally. The ongoing law enforcement exercise
against illegal logging has contributed to a shortage of raw timber materials in Indonesia, thereby driving up prices especially in major cities.
The pledged was made during a news conference with the Australian Environment Minister,
Malcolm Turnbull, who was in Jakarta to discuss a new World Bank-backed fund
aimed at countering global warming through the protection of forests (see TTM 12:6). Programmes for the fund were
still under discussion but might include reforestation as well as satellite-monitoring of the illegal logging problem.
Indonesia wants rich countries to pay developing nations to preserve their forests and plans to push this proposal at
an UN conference on climate change to be held in the Indonesian resort island of Bali in December. Mr.
Turnbull said forestry should top the agenda at that meeting.
Chinese dealers express interest in Indonesian furniture
The Indonesian Trade Attach¨¦ to China, Imbang Listiyadi, announced at the recent ¡°Twentieth Shenzhen
International Furniture, Home Decoration, Material Accessory Expo¡± (SIFE) that some mainland Chinese
businesses expressed interest in Indonesian furniture. They were keen to import Indonesian ethnic furniture, despite of
the fact that China is the world¡¯s largest furniture exporter.
A total of 108 Indonesian furniture manufacturers and members of the Indonesian Furniture and Handicrafts
Association (ASMINDO) joined the annual expo which was held in Shenzhen on 19-22 March 2007. Visitors to
the Indonesian stand were mainly from the EU, the USA, and Southeast Asian and Middle-Eastern countries. The
Indonesian furniture stand attracted 55,513 visitors, up
21% from 2006. Mr. Imbang informed that ASMINDO was keen to set up an Indonesia House in China and sign a
memorandum of understanding (MoU) with the Shenzhen Furniture Trade Association
(SFA) on a furniture design and market penetration programme.
5.
MYANMAR
DLH phases out Myanmar teak
International hardwood trader DLH Group announced that it was phasing out Myanmar teak after deciding that
sources in the country would not be able to provide the human rights guarantees demanded in its Good Supplier
Programme (GSP), TTJ informed. The announcement was made at the company¡¯s 2006 annual report released recently. The company said it would withdraw the species
gradually and completely by 2011. Myanmar teak made up only 1% of DLH turnover in 2006.
With regards to plantation teak as an alternative, DLH acknowledged that some customers, notably boat builders,
might not readily accept it due to colour, oil content and dimension considerations.
6. PAPUA
NEW GUINEA
PNG industry moves towards legality verification
The PNG Forest Industry Association (PNGFIA) is working with the Swiss firm SGS (Societe Generale du
Surveillance), one of the world¡¯s most credible inspection and verification auditors. Under a new pilot
programme, the PNGFIA and SGS will assist PNGFIA members in joining the Timber Legality and Traceability Verification
(TLTV) programme. The TLTV programme is a service
designed by SGS that ensures timber has been legally acquired, processed and traded by a particular company.
PNGFIA president, Tony Honey, said that the implementation of the programme meant the PNG industry
would be able to ¡°constructively engage with the key stakeholders, including civil society, commercial business
organizations and NGOs on the future of PNG's forest industry.¡± The Australian Minister for Fisheries, Forestry
and Conservation, Senator Eric Abetz, applauded the
development, saying that the programme complemented the Australian policy to reduce the amount of illegal
timber being imported to Australia. The Australian Timber Importers Federation also gave its support to the
programme. The move was particularly welcomed by the ANZ Bank as some of its clients are PNG forestry companies.
7. BRAZIL
Santar¨¦m asks assistance to prevent stoppage and lay-offs
The Santar¨¦m Lumber Industry Association (ASIMAS) requested the municipal administration assistance to obtain
a representation of the Environmental State Secretariat (SEMA) in Santar¨¦m, Par¨¢. The move was intended to
facilitate the evaluation of forest management plans for the state¡¯s west region and prevent production stoppage and
lay-offs. The sector demands the definition, by the State Government, of a harvest plan for 2007, including the
approval up to May of all forest management projects under analysis by the Executive Secretariat of Science,
Technology and Environment (SECTAM), followed by environment licensing of settled areas.
Wood products are major export earners in Mato Grosso
The solid-wood industry is the third largest export earner in Mato Grosso with $195 million (243,200 ton) in 2006,
according to the International Business Center (CIN) of the Industry Federation of the state (FIEMT). In the first
two months of this year, export of these products reached $30.1 million (35,300 ton), up 40% (up 28% in volume)
from 2006. Solid-wood products account for 4.5% of the
state exports. Most of the wood product exports are sawnwood and plywood, mainly to the USA and Europe.
Sinop is the main forest production cluster in Mato Grosso, accounting for 19% of the state exports in 2006,
followed by Ju¨ªna (8.4%), Aripuana(7.6%), Colniza (5.9%) and Alta Floresta (5.4%). The State Environment
Secretariat has stressed the importance to invest more in furniture and other added-value products. A large volume
of the wood raw materials of the state is shipped to other states for processing.
Revenue of furniture industry grows despite weak dollar
Despite a weak US dollar that hit exports, revenues of the Brazilian furniture sector increased in 2006. The revenue
grew 17.3% in 2006, reaching 14.13 billion reais ($6.6 billion), according to the Brazilian Association of
Furniture Companies (ABIM¨®VEL). Minas Gerais was the state with the highest growth in furniture exports,
growing 47% in 2006, followed by São Paulo (up 22%).
The strong growth was due mainly to the economic stability, improvement of family income and credit supply,and a lower interest rate. The furniture sector has high
expectations for 2007.
Brazil announces internet plan to protect the Amazon
A move to provide free internet access to native Indian tribes to help protect the Amazon rainforest from illegal
logging has been announced in Brazil. The Environment Minister, Marina Silva, said land protection was the key
aim of the plan, which would provide satellite access to 150 isolated regions. Indigenous communities were the
true protectors of their areas, she said.
Thirteen areas have been chosen by the Environment Ministry, the National Indian Foundation (Funai) and
Ibama. These include the Pantanal wetlands, the largest remaining wetland in the world largely unaffected by
human activities. Environment Ministry official, Francisco Costa, said the goal was to encourage indigenous peoples
to join the authorities in the environmental management of
the country. He said the government intended to strengthen a four-year-old digital system for monitoring
and protecting the forest called the Forest Peoples' Network. Indigenous leaders have expressed support for
the programme.
8. PERU
Peru and Chile unite to penetrate Asian market
PROMPEX (Commission for Promotion of Peruvian Exports), its Chilean counterpart ProChile and the Peru-Chile Commerce Chamber organized recently the
Seminar ¡°Peru-Chile: a joint glance to China¡± in Lima. The purpose of the seminar was to promote strategic
alliances and business aimed at increasing joint and complementary exports to China and other Asian markets.
The event gathered 180 guests, including senior executives from gremial associations and government
authorities from the forest sector as well as agro-exporters and executives from Peruvian and
Chilean companies. The speakers were part of a public and private mission, led by PROMPEX and ProChile, which visited Shanghai
in late November 2006. The aim of the mission was to identify business opportunities for companies of the two
countries and to evaluate in situ the feasibility of carrying out joint activities in order to promote exports. The
agenda of the mission included meetings with enterprises, supermarkets sale directors, forest products importers,
food importers and some Shanghai enterprise associations.
Seminar on forest management in concessions held
A seminar-workshop on ¡°Monitoring of management operations in concessions for wood based products¡± was
held in Lima in March 2007. The event was organized by the Forest and Wildlife Intendancy of INRENA in
association with CIFOR and directed to forest concessionaries form Ucayali, Madre de Dios and Loreto.
The main objective of the event was to guide concessionaires on how to improve the implementation of
forest management in the concession areas. The event also enabled assistants to exchange experiences and lessons
and to determine operational costs and logging impact. Problems in the implementation of forest management
were identified and possible strategies were discussed.


9. BOLIVIA
Bolivian exports of wood products continue expansion
The Bolivian wood industry has continued to expand exports in 2007. Bolivia exported $95.8 million (144,000
m3) in 2006, up 15% (up 12% in volume) from 2005. Santa Cruz, the main wood industry region, exported nearly $8 million in the first two months of 2007, up 20%
from the same period last year.

10. Guatemala
Guatemalan teak exports in first quarter 2007
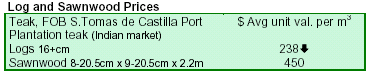
Exports of teak products reach $64,678 in the first quarter of 2007. Most of the exports were logs to the Indian
market, while there were no exports of sawnwood to India during the period.
11.
Mexico
PROTREE launched to support the forest sector
Mexico has established PROTREE, a forest program created to deal with the needs of the forest sector,
particularly forest productivity, forest recovery, funding and training. PROTREE begun operations in February
2007 and will work in 100 municipalities. Forest owners from those areas can apply for funds for forest
development projects.
Mexico allocates record budget to forest sector
The Mexican government has allocated 6 billion Mexican pesos ($546 million) to the forest sector in 2007, a record
amount. A large part of the budget will be channeled through PROTREE (see above).
Operations against illegal logging
The Ministry of Environment of Mexico DF in coordination with the Secretariat of Public Security,
Environmental Crimes section, carried out operations against illegal logging. The operations resulted in the
closure of two mills in the towns of San Miguel and Santo Tomas Ajusco, in Tlalpan.
12.
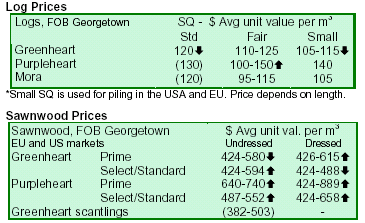
Guyana
|