|
Japan
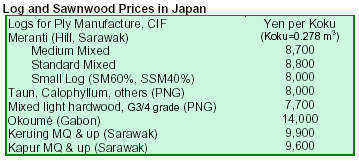
Wood Products Prices
Dollar
Exchange Rates of 28th February
2007
Japan
Yen 118.41
Reports
From Japan
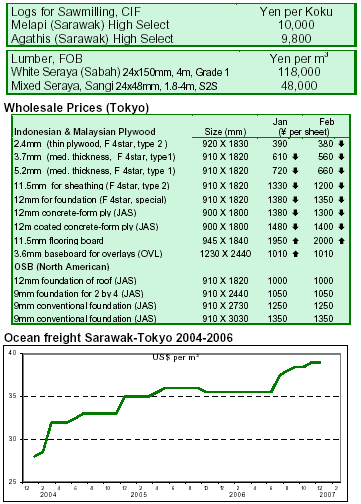
Japanese prices for tropical plywood continues correction
Sales and FOB prices of Southeast Asian plywood have been undergoing a correction over the last weeks in Japan.
Although demand is steady thanks to a mild winter, inventories are building up as arrivals of import plywood
are exceeding domestic shipments. However, imports from
Malaysia and Indonesia fell in December (see below), slowing the pace seen since last August. It is expected that
imports volumes will further decline due to dropping prices and lesser contracts. In contrast, the supply of
softwood plywood remains tight and the prices firm, which is narrowing the price gap with hardwood plywood.
=
Japanese imports of plywood surge in 2006
Plywood imports fell to 370,456 m3 in December, down 21% from November 2006 but up 15% from December
2005 (see chart).
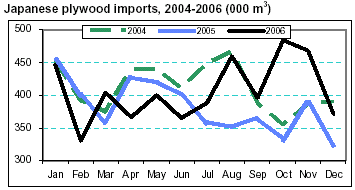
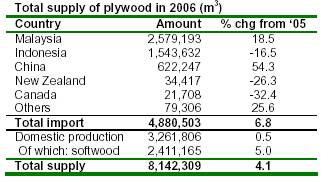
Total plywood imports rose to 4.88 million m3 in 2006
(see table), up 6.8% from 2005. By import source, 2.58 million m3 (53% of total plywood imports) came from
Malaysia (up 19% and the fifth consecutive annual increase), 1.54 million m3 from Indonesia (down 16.5%)
and 622,247 m3 from China (up 54%). Meanwhile, supply of domestic plywood surged slightly to 3.26 million m3 in
2006. Almost 74% of this domestic supply was softwood plywood.
Prospects for the supply of imported plywood in 2007
Hideyoshi Kawamura, a specialist in Japanese plywood imports, was interviewed recently by the Japan Lumber
Journal on the plywood supply prospects for Japan. He said that plywood imports from Indonesia would continue
to fall while those from Malaysia and China would rise in 2007. He said that the Indonesian government was strictly
regulating the amount of logging and, thus, the decreasing trend in production of plywood and lumber products
would continue in 2007. Assuming a log harvesting quota of 8.5 million m3 for 2007, Indonesian plywood production
would be 2-2.5 million m3 this year. Analysts predict Indonesia’s total plywood exports at 1.5 million m3 in the
future, which would affect the volume of plywood shipped to Japan. There are about 40 plywood factories currently
operating in Indonesia, of which 20 factories manufacture
products for Japan.
Demand for Malaysian logs from India, China, and other countries will continue to be strong, according to Mr.
Kawamura. Malaysia exports high quality logs and remaining log grades are sold to local plywood mills. Due
to the declining availability of high quality, big dimension
logs, Malaysia is poised to gradually shift to plantation logs, particularly from 2012-2014.
Regarding future plywood supply from China, this country is reported to have around 10,000 plywood mills. China,
the world’s top plywood exporter, exported an estimated 8.3 million m3 of plywood in 2006. Using simple
machinery and high conversion rates, about 40 million m3 of poplar and acacia boards are said to be manufactured.
The boards are priced at only $140-150 per m3. In the second half of 2006, Chinese plywood exports to Japan
decelerated due to quality problems, due particularly to the use of low-grade adhesives. Chinese boards are dried in
sunlight and, after bonding, "punctures" are common to occur. Chinese plywood manufacturers find the Japanese
JAS standards very strict and difficult to comply with. Transfer of technology from advanced plywood producer
countries is underway. Malaysia and Taiwan firms are making investment in plywood factories in mainland
China. If technology and quality improves, Japan would be able to import one million m3 of plywood from China.
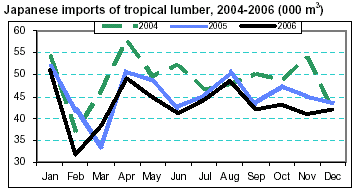
Japanese imports of tropical lumber decline
Japan’s imports of tropical lumber amounted to 42,104 m3 in December (see chart), up 3% from November but down
3% from December last year. Total lumber imports fell 5% to 517,822 m3 in 2006. Imports came mainly from
Malaysia, China and Indonesia (formerly Japan’s second
largest supplier).
|