|
1.
CENTRAL/ WEST AFRICA
Firm prices stay unchanged
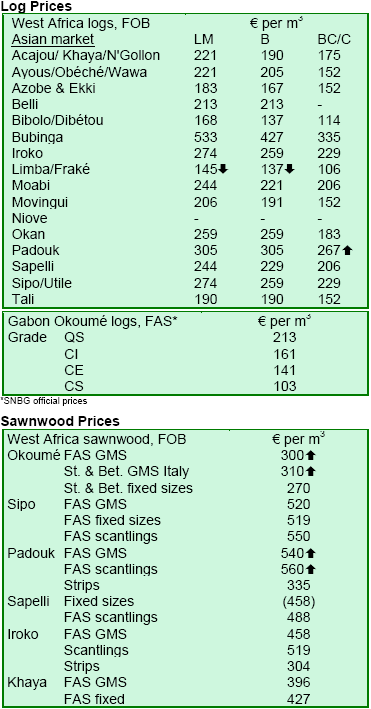
There were no significant price changes by mid-October. Trading and prices remained very stable with steady
demand from China and India. Sapele logs were in demand and prices have maintained the price levels
achieved in September.
Meanwhile, sawmills in the region continued to report good business as well as steady and firm prices. Rains
continued to affect road transport of logs and lumber in Cameroon and North Congo.
Gabon's niangon logs were priced at €220-230 per m3 FOB. There was no firm news about major progress in
resumption of log and lumber exports from Liberia, where niangon was previously a firm favourite for French
importers. There had been reports of some recent exports of niangon and other red species from the Port of Conakry,
Guinea. However, the volumes seemed to be small and there was no clear information on destinations.
Robust demand exceeds red timbers' supply
There have been some price rises of KD sapele, sipo, padouk and maobi sawnwood. Rising production costs in
African sawnmills have been the main reasons behind the price rises, according to Euwid. Higher fuel and energy
costs, in particular, are making processing and transportation more expensive while rising customs duties
and taxes are pushing costs up. Stronger European demand for sapele and sipo due to reduced meranti supply from
Southeast Asia also plays a role in the price hike. Moreover, China and India continue their competition for
larger shares of African red timber while the USA turns to sipo to replace khaya lumber.
European importers believe stocks of sapele and sipo are relatively low as a result of the strong demand. As a result,
it is increasingly difficult for European buyers to place new orders as many African sawmills are already several
months behind in deliveries. The problem is compounded
by rains in Northern Congo Basin and political instability in DRC.
New law marks new era for Liberian forests
Liberia passed a new forestry law last week, opening a new era for the Liberian forestry sector. The new
legislation will allow the implementation of Liberia's first ever forestry policy, which has been developed with the
assistance of numerous international partners through the Liberia Forest Initiative. Forest resources in Liberia are
important to its economy and constitute 47% of its land. In
the late 1990s, their contribution to the GDP amounted to about 20% and accounted for over 50% of the
country's
export earnings.
In 2003, the UN Security Council imposed sanctions on the country's diamond and timber
industries on grounds that proceeds from the sales were being used to fuel the
civil war. On 20 June 2006 (see TTM 11:12), the world body lifted the sanctions and gave the government of Liberia 90 days to pass a new legislation on forestry or
forfeit the lifting of sanction on the country.
2. GHANA
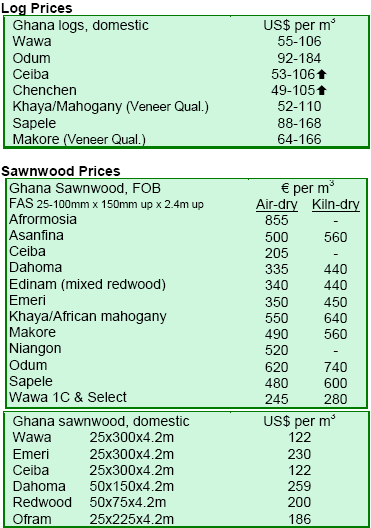
TIDD promotes alternative species in construction
Ghana's Ministry of Lands, Forestry and Mines is conducting research on the use of oil palm as lumber in the
building and construction industry, according to Mrs. Hilda Awuah-Seiwah, a manager of the Timber Industry
Development Division (TIDD) during the fourth International Building Exhibition, in Accra. Research has
already been successfully carried out on eight tree species
and plants including esia, dahoma, danta, denya, esa, afena, bamboo and coconut tree.
She informed that some 680 plants in the forests had been identified and were under study to be used in the
construction industry in place of primary timber species such as odum, mahogany, edinam and sapele, which were
facing declining availability. Research had shown that esa was harder than odum in the construction of railway lines
and in the marine sector.
Mrs. Awuah-Siwah admitted that it had not been easy to change attitudes in the construction industry with regard to
the use of the new species. She was, however, optimistic of the results of an extensive education drive, such as
exhibitions to promote the new species in the construction
and building industry.
3.
MALAYSIA
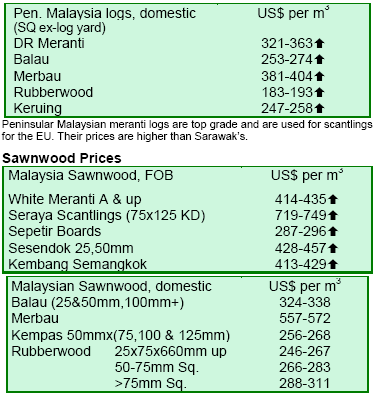
Prices retained at stable levels
Apart from logs, plywood and other panel products, prices of Malaysian timber products, especially sawnwood, were
relatively stable in the first half of October.
Plywood market bullish on soaring Japanese demand
Plywood manufacturers were enjoying a boom as Japan emerged as the main importer for most of the year and was
expected to remain so for the rest of the year. Japan was buying up to 70% of the total plywood production from
Malaysian plywood manufacturers, mainly from Sarawak.
Coconut used in plywood manufacturing
Malaysian manufacturers have successfully incorporated wood fibers from coconut trees in plywood manufacturing.
The use of coconut as an alternative source of raw material is expected to relieve pressure on oil palm plantations.
Malaysia and EU to hold more formal talks on VPA
Malaysia and the EU will hold formal talks in November to formalize the certification of timber exports to Europe,
which account for about 30% of Malaysia total timber exports. An EU delegation led by the Netherlands would
visit Kuala Lumpur next month. Malaysia and the EU had launched formal negotiations on 25 September in Brussels
(see TTM 11:16) to establish a voluntary partnership agreement (VPA) on preventing illegally produced timber
from entering the EU market. A timber licensing scheme will be set up to be used by customs authorities in
verifying the legality of imported timber. The VPA will also provide for joint studies and capacity-building. The
VPA with Malaysia would be the first agreement to be reached under the EU Forest Law Enforcement,
Governance and Trade (FLEGT) programme.
With the VPA, each timber piece would be traced based on the chain of custody, beginning from where it was
logged and from which concession to how it was taken to the sawmill, made into finished products and shipped to
which port in Europe. Plantation Industries and Commodities Minister D.P. Chin said the VPA would also
provide Malaysia a competitive edge over its biggest rivals in Asia such as Indonesia, China and Vietnam.
El Niño causes havoc to log extraction
The raw material supply situation is becoming critical for producers in West Malaysia. El Niño has not created the
dry spells in Malaysia as anticipated. So far, it has brought torrential thunderstorms across the country instead. With
the year-end monsoon season around the corner, extracting timber from the forests will be a daunting task for timber
producers.
Meanwhile, leaders from the various timber trade associations in West Malaysia have unanimously called on
the government to help address the tight raw material supply situation. It is likely that the Malaysian Timber
Council (MTC) would be assigned the task to tackle this issue. Prices of Malaysian timber products are expected to
make gains across the board by mid-November 2006.
Timber industry briefed on developments in FTAs
The Sarawak Timber Industry Development Corporation (STIDC), the Ministry of Plantation
Industries and Commodities (KPPK) and the Malaysian Timber Industry Board (MTIB) jointly organised a briefing on Free Trade
Agreements (FTAs) recently. The briefing was on developments in trade liberalisation efforts that had been
or were being negotiated by the Malaysian government.
The ASEAN-China FTA came into force on 1 July 2003 and its main provisions included: modalities for tariff
reduction; rules of origin (RoO); removal of non-tariff barriers; and safeguard measures (i.e. to prevent antidumping).
The modalities for tariff reduction and elimination for timber products are divided into Early
Harvest Programme (EHP), Normal Track (NT) and Sensitive Track (ST). Under the NT between the ASEAN
6 (Singapore, Brunei Darussalam, Thailand, Philippines, Malaysia and Indonesia) and China, all tariffs will be
eliminated by 1 January 2012. Malaysia has placed all
timber products under NT, except plywood which has been placed under ST.
The ASEAN-Korea FTA was launched on 1 July 2006. Malaysia has placed all timber and timber products under
NT with tariff elimination scheduled in 2010, except for tariff on plywood which will be eliminated in 2012.
Malaysia's position on Rules of Origin, timber is to follow the general rule i.e. Regional Value Content 40% or
Change in Tariff Heading (CTH, change in the first 4 digits).
The Malaysia-Japan FTA came into effect in July 2006, with both countries having their own agreed modality for
tariff reduction and elimination of tariff lines. Malaysia is also negotiating FTAs with the USA, Pakistan, Australia
and New Zealand. The Malaysia-USA FTA is expected to be completed by early 2007. Products Specific Rules
(PSR) would be negotiated: RoO for timber products would be based on CTH, plywood on CTH or Value
Added (VA) 40% and furniture on Change in Tariff Subheading (CTSH, change in the first 6 digits). Malaysia
has requested the USA to place all timber products under NT, with tariff to be reduced within 10 years, except for
tariffs for mouldings, plywood, fibreboard and builders'carpentry joinery, which are to be placed under EHP
(before FTA implementation). Malaysia has offered to place all Chapter 44 timber products under NT, for tariffs
to be reduced gradually within 10 years.
In the case of the Malaysia-Australia/New Zealand FTA negotiations, the general RoO for timber and timber
products would be CTH, but Malaysia has requested CTH or VA 40% for plywood and CTSH for furniture. Malaysia
has also proposed that tariffs for all timber and timber products under Chapter 44 be reduced to zero under NT by
2015.
At the ASEAN level, FTAs are being negotiated with India, Japan, Australia and New Zealand. Malaysia is
trying to build the ASEAN-Japan FTA negotiations on the Malaysia-Japan FTA.
Malaysia chalks gains in certified timber products
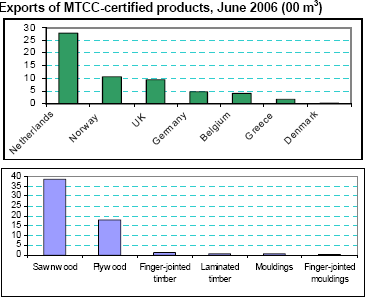
Exports of MTCC-certified timber products amounted to 5,903 m3 in June 2006. The main markets were the
Netherlands (48% of the exports), Norway (18%) and the UK (16%). Sawnwood (65%) and plywood (30%) were
the main export products. Malaysia cumulative exports of certified products since July 2002 had reached 89,933 m3.
Malaysia requested to report on 2006 ramin quotas
The 54th meeting of the Standing Committee (SC-54) of CITES recently convened in Geneva considered the
harvesting of ramin. The EU urged Malaysia to significantly lower 2007 quotas and proposed a further
review at future SC meetings. The SC agreed to continue the request to Malaysia, Indonesia and China to report to
future SCs and asked Malaysia to submit its report on
2006 quotas to the Secretariat. It further agreed to revisit the issue at SC-56 in 2008.

4.
INDONESIA
Prices retreat amid slowdown in construction
Prices of Indonesian timber products continued to fall across the board with domestic construction projects
grinding to almost a standstill during Ramadan. The general lack of security at worksites had prompted
contractors not to stockpile any timber on site until the fasting month was over and work resumed.
Indonesian ply mills cut prices to remain competitive
Years of neglect in the Indonesian plywood industry was throwing the industry into disarray. With aging equipment
and lack of proper and adequate infrastructure, Indonesian plywood manufacturers were finding it difficult to
compete with plywood manufacturers in Sarawak for the Japanese, Chinese and the emerging Indian market. As a
result, some Indonesian plywood manufacturers had
resorted to price undercutting to remain competitive. There were concerns that illegal logged timbers might end
up in the supply chain in such a situation.
Help to Indonesian fire conditional to pact ratification
Southeast Asian nations failed on 13 October to agree on a detailed plan to tackle Indonesian forest fires, urging
Indonesia to ratify an ASEAN anti-haze pollution pact before it could expect aid.
Environment and other Ministers from Indonesia, Singapore, Malaysia, Thailand
and Brunei held an emergency meeting on the issue last Friday.
Indonesia had appealed at the meeting for help to fight the forest and brush fires that have spread smoke over much
of Southeast Asia, triggering fears of a repeat of months of choking haze in 1997-98 that cost the region billions in
economic losses. One official estimated the fires raging in
parts of Sumatra and Indonesia's part of Borneo island had so far cost the country $1 billion in economic damage this
year. Indonesia's neighbours were growing increasingly frustrated with
Indonesia's failure to tackle the annual dry
season fires, most of which were deliberately lit by
farmers as well as timber and oil palm plantation owners.

5.
MYANMAR
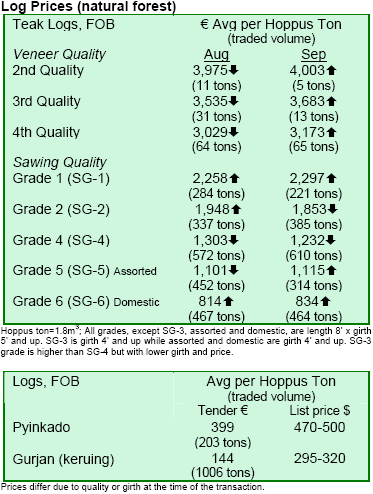
Demand for teak logs shows resilience
The teak log market remained active. Demand was good against supply despite some buyers saying that the log
grades were poor. The next teak log tender will be on 30 October. Meanwhile, the pyinkadoe market was very
weak. Some buyers claimed that substitutes from PNG and
Africa were replacing pyinkadoe. The market for gurjan remained dynamic only for fresh logs.
6. PAPUA
NEW GUINEA
Forest Authority holds regional seminar on FLEG
The PNG Forest Authority recently held a South Pacific Regional Seminar on Forest Law Enforcement and
Governance (FLEG) attended by several stakeholders and international bodies, including ITTO, World Bank,
SGS, CIFOR, Australia¡¯s Department of Forestry and the EU. The seminar will serve as an input to a study of forest law
enforcement in PNG being funded by ITTO. Highlights of some of the presentations made at the seminar will be
presented at the next issue of the TTM Report.
7.
BRAZIL
Rainy season heralds tight timber supplies
The beginning of the rainy season has brought concerns to the solid-wood industry in Northern Mato Grosso. Long
distances and poor road conditions during this period made companies intensify their operations to maintain raw
material supplies. However, the region's Lumber Industry Union (SINDUSMAD) conceded that a large number of
companies were already with low supplies. The sector had also been apprehensive as a result of a number of factors,
including delays in approval of forest management plans by the government and the strong appreciation of the real
against the US dollar. Sinop is a major forest industrial cluster in the region with timber sales of 111 million reais
in the year to August, accounting for 20% of the total trade state-wide. About 50% of the production is exported,
making it the largest exporting sector of the state.
Intensified IBAMA operations net largest ever seizures
Ibama was implementing a number of operations against environmental crimes as part of the Amazon deforestation
prevention and control plan of the federal government. During a week-long operation in late September,
Ibama's
Kojima Operation seized nearly 15,000 m³ of unlicensed
timber of different species (ipe, jatob, massaranduba and muitacatiara) in Para, probably the largest seize ever in the
state. The operation involved 30 control agents, 53 environmental policemen, 23 vehicles and one IBAMA
aircraft, all combating illegal harvesting, transportation
and wood storage. The Kojima Operation closed four of the eleven inspected lumber companies and issued 14 penalties totalling 1.1 million
reais. Ibama's former
Guariba Operation had seized 8,500 m³ of sawnwood and logs in a three-week action in Mato Grosso. The Kojima
Operation would continue in the region until December or even be extended.
Slowing US economy hits Brazilian furniture exports
Furniture sales reached $628.6 million in the year to August, down 9% from 2005. The overall projection for
2006 is a 12% decrease from $990.4 million in 2005. Firms blame the exchange rate policy and the tax burden
for the loss of shares in key markets, such as the USA, the major destination of the Brazilian furniture. According to
the Brazilian Association of Furniture Industry
(ABIMOVEL), some furniture producers had halted exports while others were selling at a loss, in expectation
of a change in the exchange rate.
Imports to the USA, which accounts for about one-third of Brazil's total furniture shipments, have fallen 26% to
$204.7 million in the year to August. Rio Grande do Sul's furniture exports to the USA are almost halved to $30.5
million in the period. According to the Association of Furniture industries of Rio Grande do Sul (MOVERGS), a
number of factors are affecting exports to the USA. These
included the US economy slowing down, domestic problems with furniture distribution in the USA and
competition from China and, recently, Colombia. The Association noted that there are still opportunities for
selling furniture this year during the High Point Fair in North Carolina and for the approaching Christmas season.
Commercial agriculture is top driver of deforestation
Recent findings have shown that direct conversion of forest to cropland in Mato Grosso reached 540,000 ha
during 2001-2004, peaking at 23% of all the deforestation in 2003, according to a study led by the US University of
Maryland. The findings indicate a shift in deforestation from the traditional cattle-ranching and small-plot farming
uses toward large-scale agriculture. The study found that clearings for cropland averaged twice the size of clearings
for pasture while conversion took place rapidly with more than 90% of the clearings planted in the first year after
deforestation. Deforestation for large-scale cropland accounted for 17% of forest loss in large clearings. The
area deforested for cropland and average soybean prices were directly correlated, suggesting that deforestation
could rise should international crop prices climb.

8. PERU
CITES to identify specific actions for mahogany trade
The 54th meeting of the Standing Committee (SC-54) of CITES was convened in Geneva, Switzerland, from 2-6
October 2006. The SC considered bigleaf mahogany trade in Peru and ramin trade in Malaysia. The US, supported by
the EU, proposed the SC to identify specific actions that
Peru must take by SC-55, with SC-55 reconsidering the issue and, if compliance is deemed unsatisfactory,
recommending a trade ban at COP-14. The SC agreed, inter alia, to address bigleaf mahogany trade in Peru at
future SC meetings.
The SC requested the Secretariat to visit Peru to review progress and report to SC-55. The SC-55 will be held on 2
June 2007, in The Hague, the Netherlands, immediately prior to COP-14 which will be held from 3-15 June 2007.
9. BOLIVIA
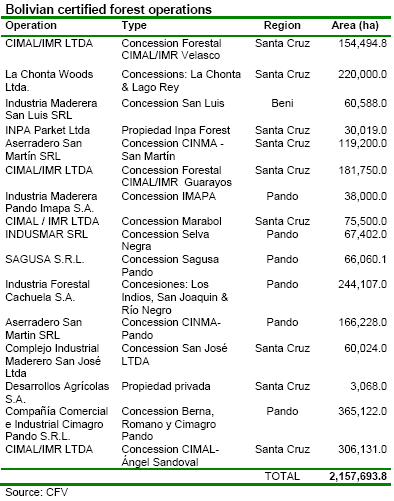
Certified Bolivian forests exceed 2 mil ha mark
The certified forest area in Bolivia totals 2,157,693.8 ha, making it the
world's largest area in the tropics certified
by FSC and one of the largest natural tropical forests to be certified. The area covers 16 certified operations of which
14 are concessions (98% of the area) and two private
properties (2%). In addition, there are 26 FSC chain-of-custody certifications, of which 23 are firms
producing sawnwood, parquet, furniture, doors, windows and two more are artisan workshops.

10. Guatemala
US swaps Guatemalan debt for forest protection
The USA will forgive about 20% of the $122 million debt owed by Guatemala to be used to protect threatened plants
and wildlife. The deal is the largest amount of debt forgiven under the 1998 US Tropical Forest Conservation
Act, which allows debt owed to the USA to be invested in protecting the environment. Over $24 million would be
set aside to sponsor conservation projects in the next 15 years in Guatemala's rain forests, mangrove reserves and
volcanic mountain chains. In recent years, Guatemala's national parks have been threatened by slash-and-burn
agriculture and land grabs.

11.
Guyana
Guyana expects higher earnings from wood exports
The total value of wood products exported from Guyana reached $41.64 million at the end of September 2006.
This was equivalent to 86% of the total exports in 2005. The main export products were sawn lumber (38% of the
exports), logs (37%) and plywood (16%). It is expected that the value of exports for 2006 would surpass the value
for 2005.
FPMC steps up aggressive campaign for timber exports
The Forest Products Marketing Council (FPMC) continued its aggressive marketing and promotion
campaign in the Caribbean and North America to promote Guyanese wood products and lesser used species. A
shipment of sawn cumaru (known as tonka bean in Guyana) was recently sent to the USA, probably the first
shipment ever of this species in sawn lumber. FPMC expected this trend to continue for other species and other
products such as decking.
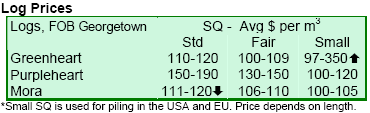
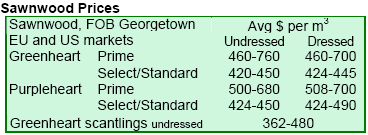
|