|
Tight methanol supply exerts pressure on resin prices
The methanol market situation has reversed in recent weeks after several stoppages and production problems in
July and August have led to production cuts at global level. Two large plants, Atlantic Methanol Production
Company LLC (AMPCO, based in Bioko Island, Equatorial Guinea) and Methanol Holdings Trinidad Ltd
(MHTL, based in Trinidad and Tobago) have temporarily shut down. Methanol is used for the production of formaldehyde and formaldehyde resin used by the woodbased
panel industry.
The reduction in methanol supply has trimmed down the deliveries of adhesive and impregnating resin in North
America to 60-70%. Spot prices of methanol have risen from $0.80 to $1.35 and in some cases $2 per gallon.
In Europe, stoppages in two German methanol plants have also reduced supply. As a result, methanol prices have
jumped from euro250 to euro350-400 per ton in the European market. It is a matter of time for prices of adhesive and
impregnating resin to rise, which would exert pressure on panel production costs.
IMF warns risks of severe global slowdown
The world is set to enjoy a 4.9% growth next year (a fifth record year high), but the risks of a sharp slowdown have
significantly increased, according to the IMF. The Fund said that the world economy is on track to grow at 5.1% in
2006 but there is a one-in-six chance of growth falling
below 3.25% in 2007. The IMF warns slower growth could be triggered by a sharp US housing market
slowdown or by surging inflationary expectations that forced central banks to raise interest rates. The report is
based on the IMF¡¯s World Economic Outlook, which come ahead of the G7 finance ministers¡¯ meeting in
Singapore on 15 September.
The report points to G7 economies slowing from 2.9% in 2006 to 2.5% in 2007. Although there have been warnings
in previous years, it is the first time IMF has warned so strongly about such a sharp potential slowdown. IMF
clarifies that there is considerable uncertainty about whether the global economy would achieve a soft landing
to a more sustainable pace of expansion or whether the world would face a period of sharply slower growth. It
adds that tight commodities markets are contributing to inflation concerns and the risk of a growth slowdown. IMF
indicates that, for that reason, further monetary tightening could not be ruled out in the USA, while in the euro area,
some further tightening would likely be needed to maintain price stability in the
medium run.
Review shows falling US wooden panel exports
Exports of US wooden panels were down in 2005, mainly due to a robust housing market which acted as a
disincentive for panel producers to aggressively pursue opportunities in foreign countries. Furthermore, rising
supplies of panels from low-cost European and South American mills were hampering US exports.
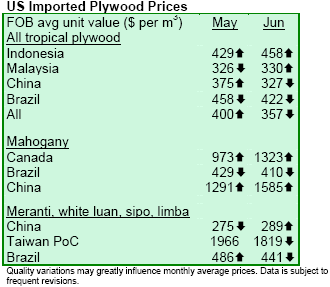
Imported plywood gains bigger market share
US exports of softwood plywood shrank 17% to 411 million square feet (sf., 3/8¡± basis) in 2005. In contrast,
US plywood imports grew 16% to 2,442 million sf., accounting for almost 15% of the entire US plywood
consumption. US imports came mainly from Brazil (65% of the total imports), Canada (22%) and Chile (10%).
OSB exports register decline for fifth straight year
North American OSB prices reached an almost historical peak in 2005. In light of the current cooling demand and rising competition from imports, OSB prices were now
weakening slightly. The buoyant domestic demand and the growing influx of European and South American OSB in
overseas markets continued to act as strong disincentives to selling OSB outside of the USA and Canada. North
American exports declined 19% to 167 million sf. in 2005, extending a five-year trend that had seen North American
exports contract at an average compound annual rate of 14%.
Particleboard/MDF exports to stay within N. America
Escalating energy and resin costs and fibre supply shortages were expected to lead to a continued decline in
North American MDF and particleboard production. In light of the increased global competition, North American
exports consist mainly of deliveries between the USA,
Canada and Mexico.
¡¡
|