US Dollar Exchange Rates of
26th June 2017
China Yuan 6.8411
Report from China
Chinese overseas investment in the timber sector
According to a report on China¡¯s Wood Products Trade
and Investment (2016) there were 167 Chinese enterprises
with overseas operations at the end of 2014. Of the total,
over 90% were private enterprises.
Private enterprises have become the main players in
overseas forestry investment and have taken a long-term
view to these investment and have the advantage of being
able to adopt quickly to changing production and trade
conditions.
The origin of the 167 enterprises identified in 2016 was in
17 provinces, autonomous regions and municipalities.
Enterprises in 5 provinces; Heilongjiang, Inner Mongolia,
Jilin, Shandong and Jiangsu p dominated the overseas
investors namely;.
Enterprises investing in overseas forestry and timber
operations are mainly from three areas, Heilongjiang
province, Jilin province and Inner Mongolia Autonomous
Region which is adjacent to Russia.
Enterprises from the Inner Mongolia Autonomous Region
invest mainly in forestry operations in Russia. The others,
mainly from the regions in China that account for much of
the country¡¯s wood product manufacturing such as Jiangsu
and Shandong provinces, invest in developing countries
mainly in raw material sourcing.
There are two main patterns of Chinese overseas
investment, one is direct purchase or lease of forest land
the other is joint venture cooperative arrangements.
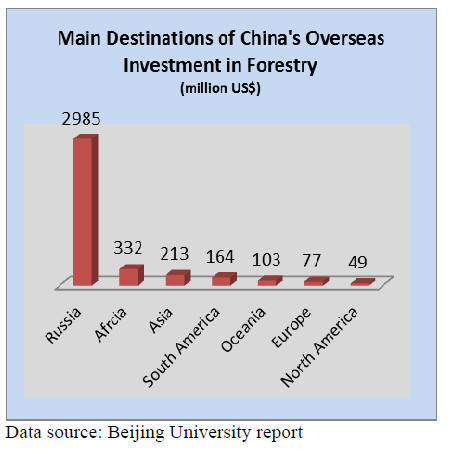
Chinese enterprises invest mainly in Russia, with smaller
investments in Gabon, Brazil, Papua New Guinea,
Australia and New Zealand and operations include
logging, primary processing and downstream
manufacturing. The distribution of investment in 2014 is
illustrated below.
Chinese enterprises say while trading is relatively low risk
the risks increase significantly with overseas investment
largely due to long term pay-back period, the complexity
of the international business environment, financial risks,
host government regulations and supervision and
environment risks.
Overseas investment by Chinese enterprises has been
increasing in recent years and the value of foreign direct
investment for Chinese forestry products industry is
expected to rise given the Chinese government¡¯s ¡°Go Out¡±
policy.
For more on this see:
https://www.cigionline.org/publications/deeper-lookchinas-
going-out-policy
As the go-out policy takes affect it is expected that
China¡¯s investment in forestry and wood processing will
become more diversified. It is anticipated that
multinational companies will emerge in the future.
It is further anticipated that the patterns of investment and
cooperation will become more diversified from traditional
direct purchasing or renting to mergers and acquisitions,
joint ventures, capital operation, strategic alliances, stock
exchange and this will lead to greater integration of
logging, intensive processing, logistics and trade.
Enterprises urged to strengthen capacity to comply
with US regulations
It has been reported that the USA Act of Formaldehyde
Standard for Wood Composite Products had been
introduced so that all composite wood products sold,
supplied and manufactured in the USA must meet the new
regulation.
Wood products are an important export product for China
and the value of wood products exports exceeded US$30
billion in 2016. Of this total, the export value of composite
wood products was US$7 billion.
The Chinese government¡¯s Inspection and Quarantine
Service has urged domestic wood products enterprises to
pay more attention to satisfying the regulations in
importing countries.
They have advised enterprises to utilise raw materials
whose formaldehyde emission comply with the standard of
wood composite products in the USA regulation.
Enterprises have been advised to establish a sound system
to control the export of toxic and harmful substances in
wood products to ensure that composite wood products
enter the US without difficulty.
The government is working to transform and upgrade
China's wood products industry to enhance added value
production. The focus is on technical training,
formaldehyde detection, improved self-inspection and
control, strengthen product innovation and design as well
as the creation of brands and image.
|